Summary: The growing importance of digitalization in MSMEs is not only the policy agenda but is also important for the survival of this segment. Digitalisation will not only improve their competitiveness, but also benefit society at large because SMEs are the main service providers in the regional economic growth and innovations.
MSMEs segment is the backbone of the Indian economy. However, in the past few years, challenges such as demonetisation, supply chain bottlenecks, financial crisis, and adopting to digital ecosystem have been rocking the MSMEs sector.
The growing importance of digitalisation in MSMEs is not only the policy agenda but is also important for the survival of this segment. Digitalisation will not only improve their competitiveness, but also benefit society at large because SMEs are the main service providers in the regional economic growth and innovations.
Though digitalisation is the buzzword today, anxieties about how to adopt it and the impact of this transformation in business are still restricting its adoption in many an organisation.
The MSME sector is critical to the growth of a country like India, especially because of its huge population, as it fosters entrepreneurship and employment opportunities. This sector reduces the problem of disguised unemployment by absorbing the agricultural labours during the lean season. This segment also extends support to the large industries in the form of ancillary units and plays a significant role in the entire value chain of the business. Since almost 51% of Indian MSMEs are based in the rural regions, the sector contributes to the economic empowerment and social inclusion of the rural population. They are engaged in diversified fields ranging from traditional rural handicrafts to technology oriented industrial units.
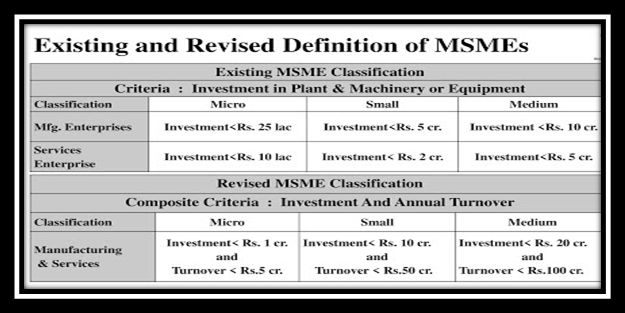
The significance of this sector is evident from the numerous government initiatives taken to boost its growth, the most significant one being the revision in the definition of the MSMEs. Global trends in classifying MSMEs revealed that most of the countries are using major parameters like number of employees, net worth, turnover, capital employed, etc. To facilitate ease of doing business the Government of India revised the definition of MSMEs vide the Gazette Notification S.O. 2119 (E) dated June 26, 2020. Accordingly, the definition of MSMEs is mentioned in the table given below: Despite the notable contribution of the MSME segment to the country’s economy, it could not evolve as a robust, resilient player. MSMEs face several challenges—availability of low cost credit facilities, procurement of raw material, inertia to technology adoption, capacity building, supply chain disruption, and the perennial problem of delayed payments, among others.
Apart from these, the COVID-19 pandemic continues to keep the world on edge. Though businesses are getting back to pre-pandemic levels, the uncertainty over the duration and intensity of the pandemic continue to cause concern. Just like boosting immunity of the population is a key to tackle the pandemic, the key to long-term sustainability for MSMEs would be to focus on innovation and digitalisation.
Seizing opportunities from digitalisation
Digital is becoming a way of life—billions of people wake up to notifications from social media sites, e-mail, etc. Opportunities provided by digitalisation are compelling organisations to look at their business models from a different perspective.
A digitalisation infrastructure can help reposition business by improving the reach beyond geographical boundaries. The era of invisible networks has created a new market for the economy at large. Information rushes through the networks at the blink of an eye, customers can pick and choose any services, products from across the globe.
Indian MSMEs and digitalisation
The MSME sector is yet to benefit from the advancements in the digital space. Anxiety and confusion about how digitalisation will impact my business, how much capital will be required for the digitalisation, the fear of failure to implement, and more such doubts are gripping the MSMEs into inaction.
Given the present scenario, more and more customers are shifting to online platforms which are providing opportunities for MSMEs to transform and build on digitalisation of their businesses. Digitalisation provides opportunity to thrive on enriched data and thereby take corrective actions on time.
Why is Digitalisation a challenge for MSMEs?
Digital literacy: The term ‘digital literacy’ means ability to use information and communication technologies to find, evaluate, create and communicate information using both analytical and technical skills. Digital transformation requires cultural and behavioural changes such as new ways of approaching customers, monitoring the digital behaviour of the customers, keeping customers engaged using digital marketing, increased collaboration with tech-savvy entities, etc. It is important to develop a mindset to embrace the change. Digital literacy is the primary step towards the ultimate goal of embracing the change and reinforcing new behaviours and way of working through the digital platforms.
Denial from workforce: Concerns about being replaced by young, tech-savvy staff, or machines are reasons enough for the workforce to oppose digitalisation. Insecurity and anxiety about the unknown may even lead to sabotaging of the process of digital transformation.
Switching Cost: A majority of the MSMEs operate on a thin margin with limited capital.
These units do not have easy access to formal credit system. Most of the firms run their business out of their own investment or by borrowing money from friends and family. These entities feel that digital transformation requires a big budget and are therefore pessimistic towards digitisation.
Loss of revenue from non-digital customers: Digitalisation is often considered as a something that will eat away the share of revenue contributed by non-digital platforms.
Cyber Security: An unsafe online environment presents another challenge in adopting a digital framework. Instances of hacking, intellectual property infringement, etc. are pose major threats.
Inconsistency in quality of customers and digital agenda: The real meaning of digitalisation is often misinterpreted. The business units assume that digital transformation means the act of using some of the digital tools along with the traditional business model. They fail to understand that it is not a momentary event, but it is something that they must sustain over the years.
Digital engagement levels of MSMEs in India
The series of struggles which the MSMEs face leads to obstruction in their way to transformation. They try to adopt reform measures on a trial and error approach. They experiment and mend things and many a times come at crossroads. In this process some reach their destination, some struggle in the initial stage, while the rest reach the mid-way and thrive to improve with perseverance and zeal.
The engagement level of MSMEs can be categorised as under:
Offline. MSMEs which do not use computers, social media platforms, and have no access to internet.
Connected. Those that have preliminary knowledge of digital platforms and are making © Shutterstock.com minimal use of digital channels like e-mails, search engines etc.
Enabled. These entities have corporate e-mail IDs, own website, and social media presence to maintain relations with their clients. They understand the market using digital platforms.
Engaged. These segments of MSMEs are tech-savvy and proficient in digital tools, predominant volume of their business activity is executed through digital platforms.
At present, over 80 per cent of the MSMEs belong to the offline and connected engagement level.
Way forward
Real digital transformation is about breaking the barriers and leveraging technology for increased earnings and profitability. There is need for effective integration of technology and all the available key resources of the business.
Acquiring digital IQ
Acquisition of Digital IQ or Digital Maturity is necessary to reap the benefits of digitalisation. It is the measurement of the organisation’s ability to harness growth and profitability from the digital framework. The journey towards digital agility is not a onetime moment; it is a continuous and enduring process. It is a thing beyond a statement like, ‘We want to go paperless’. The management must be clear about the specifics of the organisation, assess the effect of transformation on the culture and commercial side of the business and align the digital objective with the mission of the business entity.
Shift in the mindset & culture change
Regardless of the effectiveness of the digital mission, it will be truly successful, only if there is a shift in the mindset of the entire workforce of the organisation. The employees should be directly involved in the transformation process. The leader must set an example by getting actively involved in the process.
Identify the gaps
It is also important to maintain close connection with the world outside the organisation to understand the external needs, temperament of the customers, and strategies adopted by competitors. Meaningful connections needed to be established with the customers to understand the digital experience they value. From the needs of the customers, identify the digital model that will bridge the gaps of the unmet customer expectations. One method to identify the gaps can be to host a virtual event for the customers to get their feedback, experience the digital products used by the customers, etc.
Leveraging government schemes
The government is introducing several schemes and incentives for MSMEs who want to adopt digitalisation. ZED is one such scheme introduced to encourage MSMEs to adopt quality tools/systems and energy efficient manufacturing process.
Route to digital transformation
Some methods for successful digital transformations are consistency in plan, establishing flexible framework, and a collaborative approach with expert service providers like digital hubs, startup support system, etc.
Transformation is not just an agenda; it must become a natural way of working of the entity. The emerging technologies must be the core competencies of the organisation. It is important to embrace the challenges to make the journey meaningful and effective for the business.
Log In or become an AIMA member to read more articles